Intro to ROS Part 8: Using Parameters to Configure ROS 2 Nodes
2025-11-13 | By ShawnHymel
Single Board Computers Raspberry Pi SBC
One of the key strengths of ROS 2 is its flexibility. So far in our tutorials, we've built publisher and service nodes with hardcoded values, such as the message to publish or the delay between timer callbacks. While this is fine for simple prototypes, it quickly becomes limiting in real-world applications. Fortunately, ROS 2 offers a better way: parameters.
In this tutorial, we'll explore how to use parameters in ROS 2 to dynamically configure nodes. You'll learn how to set parameters at runtime, update them while a node is running, and make your nodes more reusable and adaptable. We'll implement examples in both Python and C++ using a basic publisher node that emits a message to a topic.
The Docker image and code for this series can be found here: https://github.com/ShawnHymel/introduction-to-ros
Why Parameters Matter
Parameters allow you to define and update configuration values without modifying your source code. For example, you can reuse the same node to publish different messages or at different rates by simply changing parameters. This is incredibly useful for tuning robots or adapting behaviors without needing to recompile or redeploy your software.
Parameters are defined and accessed using the rclpy and rclcpp libraries in Python and C++, respectively. When a node launches, you can specify parameters using command-line arguments or configuration files. You can also update certain parameters while the node is running, which makes them even more powerful.
Basic Parameter Use in Python
Let’s start by modifying the minimal publisher example in Python. We'll create a new file called publisher_with_params.py and define two parameters: message and timer_period. The message parameter sets what string will be published, and timer_period sets the interval between publications.
import rclpy from rclpy.executors import ExternalShutdownException from rclpy.node import Node from example_interfaces.msg import String
class PublisherWithParams(Node):
"""Publisher example that periodically sends out a string"""
def __init__(self):
"""Constructor"""
# Call the Node class constructor with the node name
super().__init__('publisher_with_params')
# Declare parameters
self.declare_parameter('message', "Hello")
self.declare_parameter('timer_period', 1.0)
# Set to attributes
self._message = self.get_parameter('message').value
self._timer_period = self.get_parameter('timer_period').value
# Create a publisher object
self._publisher = self.create_publisher(String, 'my_topic', 10)
# Periodically call method
self._timer = self.create_timer(
self._timer_period,
self._timer_callback
)
def _timer_callback(self):
"""Publishes a simple message to topic"""
# Fill out String message
msg = String()
msg.data = self._message
# Publish message to topic
self._publisher.publish(msg)
self.get_logger().info(f"Publishing: {msg.data}")
def main(args=None):
"""Main entrypoint"""
# Initialize and run node
try:
rclpy.init()
node = PublisherWithParams()
rclpy.spin(node)
# Catch ctrl+c or shutdown request
except (KeyboardInterrupt, ExternalShutdownException):
pass
# Destroy node (now) and gracefully exit
finally:
if node is not None:
node.destroy_node()
if rclpy.ok():
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Add the following executable to setup.py:
"publisher_with_params = my_py_pkg.publisher_with_params:main",
Build the package:
colcon build --packages-select my_py_pkg
When you run the node with no arguments, it uses the default parameters. But you can override them at runtime like this:
source install/setup.bash
ros2 run my_py_pkg publisher_with_params --ros-args -p message:="Hi from ROS2!" -p timer_period:=0.5
These values are only set at startup. If you stop and restart the node, it resets to the defaults unless you specify the parameters again.
You can echo the messages in another terminal:
ros2 topic echo /my_topic

Updating Parameters at Runtime (Python)
To support dynamic updates to parameters while the node is running, we can use the add_post_set_parameters_callback() method. This allows us to respond when a parameter is changed. Modify the self.__init__() method and add a self.add_post_set_parameters_callback() method to your node:
import rclpy
from rclpy.executors import ExternalShutdownException
from rclpy.node import Node
from example_interfaces.msg import String
class PublisherWithParams(Node):
"""Publisher example that periodically sends out a string"""
def __init__(self):
"""Constructor"""
# Call the Node class constructor with the node name
super().__init__('publisher_with_params')
# Declare parameters
self.declare_parameter('message', "Hello")
self.declare_parameter('timer_period', 1.0)
# Set to attributes
self._message = self.get_parameter('message').value
self._timer_period = self.get_parameter('timer_period').value
# Configure callback for runtime parameter update
self.add_post_set_parameters_callback(self._post_parameters_callback)
# Create a publisher object
self._publisher = self.create_publisher(String, 'my_topic', 10)
# Periodically call method
self._timer = self.create_timer(
self._timer_period,
self._timer_callback
)
def _timer_callback(self):
"""Publishes a simple message to topic"""
# Fill out String message
msg = String()
msg.data = self._message
# Publish message to topic
self._publisher.publish(msg)
self.get_logger().info(f"Publishing: {msg.data}")
def _post_parameters_callback(self, params):
"""Set parameter after node started"""
# Loop through all parameters
for param in params:
# Update message
if param.name == 'message':
self._message = param.value
self.get_logger().info(f"Set {param.name} to {param.value}")
# Update timer
elif param.name == 'timer_period':
# Update member variable
self._timer_period = param.value
self.get_logger().info(f"Set {param.name} to {param.value}")
# Reset timer
self._timer.cancel()
self._timer = self.create_timer(
self._timer_period,
self._timer_callback
)
# Unknown parameter
else:
self.get_logger().warn(f"Unknown parameter: {param.name}")
def main(args=None):
"""Main entrypoint"""
# Initialize and run node
try:
rclpy.init()
node = PublisherWithParams()
rclpy.spin(node)
# Catch ctrl+c or shutdown request
except (KeyboardInterrupt, ExternalShutdownException):
pass
# Destroy node (now) and gracefully exit
finally:
if node is not None:
node.destroy_node()
if rclpy.ok():
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Build the package again:
colcon build --packages-select my_py_pkg
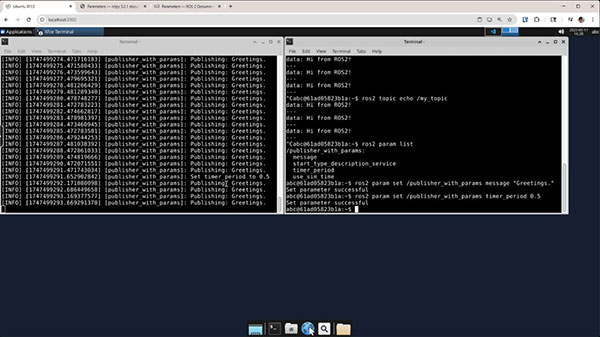
In one terminal, run the publisher:
source install/setup.bash ros2 run my_py_pkg publisher_with_params --ros-args -p message:="Hi from ROS2!"
In a second terminal, echo the messages:
ros2 topic echo /my_topic
In a third terminal, dynamically update the parameters to the publisher:
ros2 param list ros2 param set /publisher_with_params message "Greetings." ros2 param set /publisher_with_params timer_period 0.5
You should see the message text and frequency change.
Using Parameters in C++
Let’s port the same example to C++. Start with a copy of your minimal_publisher.cpp, and update it to declare, retrieve, and monitor parameters.
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "example_interfaces/msg/string.hpp"
/**
* Publisher example that periodically sends out a string
*/
class PublisherWithParams : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
/**
* Constructor (call Node class constructor with node name)
*/
PublisherWithParams() : Node("publisher_with_params")
{
// Declare parameters
this->declare_parameter("message", "Hello");
this->declare_parameter("timer_period", 1.0);
// Get parameters and set to member variables
message_ = this->get_parameter("message").as_string();
timer_period_ = this->get_parameter("timer_period").as_double();
// Configure callback for runtime parameter update
param_cb_handle_ = this->add_post_set_parameters_callback(
std::bind(
&PublisherWithParams::post_parameters_callback,
this,
std::placeholders::_1));
// Create a publisher object
publisher_ = this->create_publisher<example_interfaces::msg::String>(
"my_topic",
10);
// Periodically call method
timer_ = this->create_wall_timer(
std::chrono::milliseconds(500),
std::bind(&PublisherWithParams::timer_callback, this));
}
private:
/**
* Publishes simple message to topic
*/
void timer_callback()
{
// Fill out String message
auto msg = example_interfaces::msg::String();
msg.data = message_;
// Publish message to topic
publisher_->publish(msg);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Publishing: %s", msg.data.c_str());
}
/**
* Set parameter after node started
*/
void post_parameters_callback(
const std::vector<rclcpp::Parameter> ¶meters)
{
// Loop through all parameters
for (const auto ¶m : parameters) {
// Update message
if (param.get_name() == "message") {
message_ = param.as_string();
RCLCPP_INFO(
this->get_logger(),
"Set %s to %s",
param.get_name().c_str(),
param.as_string().c_str());
}
// Update timer period
else if (param.get_name() == "timer_period") {
// Update member variable
timer_period_ = param.as_double();
RCLCPP_INFO(
this->get_logger(),
"Set %s to %f",
param.get_name().c_str(),
param.as_double());
// Reset timer
timer_->cancel();
timer_ = this->create_wall_timer(
std::chrono::duration<double>(timer_period_),
std::bind(&PublisherWithParams::timer_callback, this));
}
// Unknown parameter
else {
RCLCPP_WARN(
this->get_logger(),
"Unknown parameter: %s",
param.get_name().c_str());
}
}
}
// Declare member variables
std::string message_;
double timer_period_;
rclcpp::Publisher<example_interfaces::msg::String>::SharedPtr publisher_;
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
rclcpp::node_interfaces::PostSetParametersCallbackHandle::SharedPtr
param_cb_handle_;
};
/**
* Main entrypoint
*/
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
// Initialize ROS 2
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
// Initialize and run node
auto node = std::make_shared<PublisherWithParams>();
rclcpp::spin(node);
// Cleanup
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
Add the executable to CMakeLists.txt
# Define trigger_points_client target and link libraries
add_executable(publisher_with_params src/publisher_with_params.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(publisher_with_params rclcpp example_interfaces)
# Install binaries to specific folder
install(TARGETS
minimal_publisher
minimal_subscriber
minimal_server
minimal_client
acc_subscriber
trigger_points_client
publisher_with_params
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})
Build the package:
colcon build --packages-select my_cpp_pkg
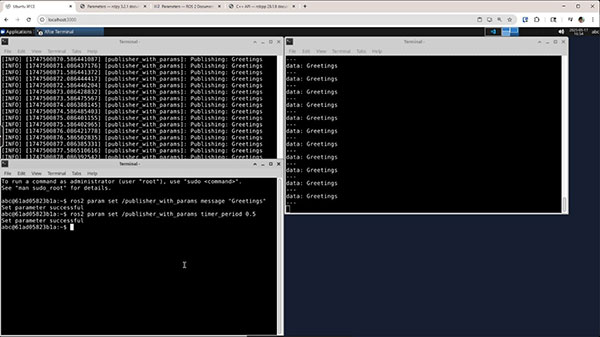
In one terminal, run:
source install/setup.bash ros2 run my_cpp_pkg publisher_with_params --ros-args -p message:="Hi from ROS2!"
In a second terminal:
ros2 topic echo /my_topic
In a third terminal:
ros2 param set /publisher_with_params message "Greetings." ros2 param set /publisher_with_params timer_period 0.5
Just like with the Python example, you should see the message and frequency change.
Summary
In this tutorial, we explored how to use parameters in ROS 2 to make your nodes more flexible and configurable. We learned how to declare parameters, read them at startup, and update them at runtime using both Python and C++. Parameters are a key part of writing robust and reusable ROS 2 applications, especially in scenarios where tuning and runtime adaptability are critical.
By using parameters, you eliminate the need for recompilation or editing source code just to change configuration values. This leads to cleaner, more maintainable codebases and a smoother development workflow. As your projects grow in complexity, the ability to dynamically configure nodes becomes increasingly important. In the next part of the series, we'll look at launch files and how to orchestrate complex systems using parameterized configurations.
Stay tuned!